ASME Section 8 is a code that provides the standards and guidelines for the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) developed this code to ensure that pressure vessels are safe and reliable in their operation. It is used by engineers, manufacturers, and inspectors who are involved in the design and fabrication of pressure vessels.
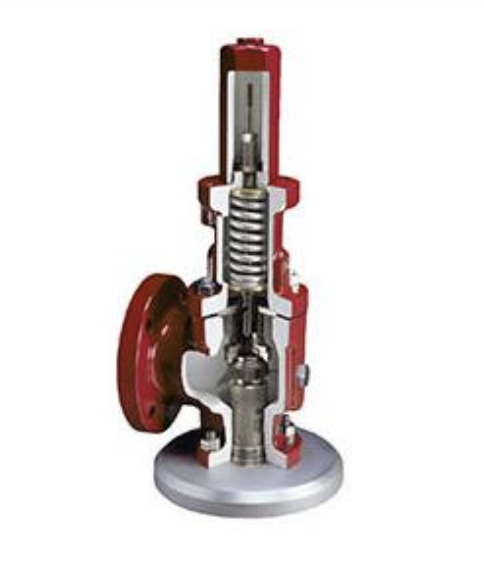
Pressure vessels are containers that are used to store or transport gases or liquids at high pressures. Examples of pressure vessels include boilers, tanks, and piping systems. They are used in a variety of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation. Because of the high pressures involved, pressure vessels must be designed and manufactured to strict safety standards.
ASME Section 8 is divided into three divisions: Division 1, Division 2, and Division 3. Each division provides different requirements based on the intended use of the pressure vessel.
Division 1 is the most commonly used division of ASME Section 8. It covers the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels that operate at a pressure of 15 psi or higher. This division provides the minimum requirements for pressure vessels and is used for most applications. Division 1 includes rules for materials, design, fabrication, examination, inspection, testing, certification, and pressure relief.
Division 2 is an alternative set of requirements for the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels. It is intended for pressure vessels that operate at a pressure of 15 psi or higher, but with more stringent requirements than Division 1. Division 2 includes rules for materials, design, fabrication, examination, inspection, testing, certification, and pressure relief. It also includes rules for nonmetallic vessels, such as those made of composites.
Division 3 provides requirements for the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels that operate at a pressure of 10,000 psi or higher. This division is used for specialized applications, such as nuclear power plants and aerospace systems.
ASME Section 8 provides a comprehensive set of rules and guidelines for the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels. It covers every aspect of pressure vessel design and construction, from the materials used to the pressure relief systems installed. By following the standards outlined in ASME Section 8, engineers and manufacturers can ensure that their pressure vessels are safe and reliable.
One of the key components of ASME Section 8 is the design of pressure vessels. The code provides rules for the design of pressure vessels, including the materials that can be used, the thickness of the walls, and the shape of the vessel. The design must take into account the intended use of the pressure vessel, the pressure it will be subjected to, and any other factors that may affect its performance.
ASME Section 8 also covers the fabrication of pressure vessels. This includes rules for welding, forming, and heat treating the materials used in the pressure vessel. The code provides guidelines for the inspection of pressure vessels during fabrication to ensure that they meet the required standards.
The inspection and testing of pressure vessels is also a critical aspect of ASME Section 8. The code provides guidelines for the inspection of pressure vessels during fabrication and after they have been put into service. This includes guidelines for visual inspection, radiographic testing, and ultrasonic testing, among others.
In conclusion, ASME Section 8 is an important code that provides the standards and guidelines for the design, fabrication, inspection, testing, and certification of pressure vessels. It is used by engineers, manufacturers, and inspectors to ensure that pressure vessels are safe and reliable in their operation.